tibial torsion test name|femoral anteversion and tibial torsion : importers Orthopedic Exam/ Special Test: Ramirez’s Test PROCEDURE: patient is supine, . webBalls444 1yr ago #447200. There's a higher-quality version here: https://watchpeopledie.tv/h/gore/post/10155/classic-the-infamous-yo-quiero-agua. I feel .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBO Portal do Paciente - AmorSaúde é uma ferramenta online que permite aos pacientes agendar consultas, exames, telemedicina e acessar seus resultados e histórico médico. Cadastre-se gratuitamente e aproveite os benefícios de cuidar da sua saúde com amor e .
Tibial torsion causes the feet to turn inward, or have what is also known as a “pigeon-toed” appearance. The ability to compensate for tibial torsion depends on the amount of inversion and eversion present in the foot and on the amount of rotation possible at the hip.
clunk test for labral tear
Special Test: Mortons Neuroma aka Metatarsal Squeeze Test: Video .A positive test will result in laxity and/or pain Sensitivity 67, Specificity 75, LR+ 2.7, .Orthopedic Exam/ Special Test: Ramirez’s Test PROCEDURE: patient is supine, .
Heel Thump Test: PROCEDURE: the patient is in seated or supine; the .Deltoid Ligamentous Stress Test: (Passive Relaxed) - Assess Anterior, Middle and .Special Test:Posterior Drawer Test (Ankle) PROCEDURE: •Patient is supine with .
Anterior Drawer Test – (Ankle): POSITIVE TEST: Excessive anterior translation. .
Tibial Torsion Test; Tinel’s Sign (Ankle) Thompson’s Test / Simmond’s Test. .
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .
Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance.Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A physical exam can diagnose tibial torsion. .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shin bones (the bones that are located between the knee and the ankle). Tibial torsion causes the child's feet to turn inward, or have what is also .
Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone and the knees flexed to 90 °. Typically the foot axis is 10 ° .
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A .Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with . Dr. Rome explains the proper technique to determine if a patient exhibits any degree of external tibial torsion.Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equ.Tibial torsion can happen because of the position of the baby in the uterus. It also tends to run in families. . At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. . Know why a test or procedure is .
Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equilibri.
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. . At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you for your child. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and .
tibial torsion special test
Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, and about two thirds of patients are affected bilaterally. [1, 2] Tibial torsion can persist into adulthood and give rise to patellofemoral pathology.Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. . write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. . Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. If your child has a follow-up appointment, write . trochanteric prominence angle test . . tibial torsion. look at thigh-foot angle in prone position. normal value in infants- mean 5° internal (range, −30° to +20°) normal value at age 8 years- mean 10° external (range, −5° to +30°) metatarsus adductus.
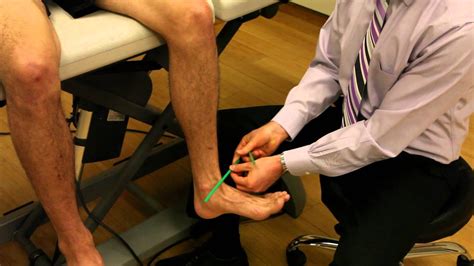
Tibial torsion was calculated by subtracting the proximal tibial angle from the distal tibial angle. . Continuous variables were checked for normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and presented in the form of mean ± SD (standard deviation). . Name must be less than characters Choose a collection:Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test (TPAT)'. Femoral anteversion is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur. It is also known as Femoral neck anteversion. Tibial torsion test in sitting position. Tibial torsion is measured by having the patient sit with the knee flexed to 90’over the edge of the examining table. The examiner has put the thumb of one hand over the apex of the one malleolus. Next, the examiner visualizes the axes of the knee & of the ankle.Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .
External Tibial Torsion: - Knees face outward, often leading to a wider stance. - This places extra stress on the outer knee and hips. - Squat depth and stability are compromised due to improper muscle loading. Lunging with Tibial Torsion. Lunges demand stability and alignment, both of which are challenged by tibial torsion: Internal Tibial .
Internal tibial torsion is one cause of intoeing. With internal tibial torsion, the shin bone (tibia) is slightly twisted or rotated, causing the foot to turn in. This may be due to the position your child was sitting in while in the uterus. Intoeing due to internal tibial torsion is generally most noticeable when a child begins walking.Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. Craig's test is described in detail here. . Thigh-foot angle (TFA): a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure .
Tibial torsion can happen because of the position of the baby in the uterus. It also tends to run in families. . At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. . Know why a test or procedure is . What causes tibial torsion? Tibial torsion tends to be hereditary and can be passed down from parents to children. The position of a fetus in the uterus can also make a child more likely to have tibial torsion. What are the symptoms of tibial torsion? The "in-toeing", or walking with the toes pointed inward, is the primary symptom of tibial .
By mid-childhood, a small percentage of children will continue to have significant tibial torsion. How is tibial torsion diagnosed? Tibial torsion is diagnosed (and distinguished from other causes of in-toeing) by a careful physical exam. Tibial torsion is assessed by measuring the thigh-foot angle, if the foot is shaped normally. Physical exam test procedure for examination of the foot and ankle and associated structures.
Introduction. Since Staheli et al. described rotational profile, TFA and TMA have been used predominantly to measure tibial torsion [20, 21].In patients with CP and myelomeningocele, to eliminate external tibial torsion, tibial derotation osteotomy frequently is performed [4–6, 19, 22].Because physical measurements are obtained easily in outpatient, . Internal tibial torsion is most frequently bilateral, and may at times present with metatarsus adductus, femoral anteversion, or physiologic bow legging. Pertinent clinical findings on examination include a forward or outward-facing patella, or in a seated position, there may be a posterior rotation of the medial malleolus (in comparison to the . Normally, lateral rotation of the tibia increases from approximately 5º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity; femoral anteversion decreases from approximately 40º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity. Tibial torsion Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of intoeing.
Wilcoxon's rank sum test was used to determine differences between goniometric and CT measures for tibiofibular torsion. No significant difference for goniometric measures was found between testers for tibiofibular torsion or TFA. A significant difference averaging 5° between goniometric and CT torsion measures was found between testers. Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. . write down the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. . Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. If your child has a follow-up appointment, write .
Tibial torsion specifically is either the internal or external rotation of the lower leg bone (tibia). With equal incidence in both males and females, 1 internal tibial torsion occurs most commonly in the womb, as the legs internally rotate to fit in the space. Tibial rotation is the rotation of the entire tibial shaft (bone) which takes place in gait as the foot pronates and supinates. The Tibia can exhibit both torsion and rotation and this makes this subject both interesting and somewhat difficult. Tibial torsion occurs where the tibia exhibits a twist in the actual bone and is apparent from birth. Tibial torsion is a twist in the tibia measured as an angle between a proximal axis line and a distal axis line. . samples and 3 raters were used for the reliability study. 21 Data were assessed for normality using a Shapiro-Wilk test. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) estimates were calculated based on a mean rating (k = 3), absolute .
tibial torsion in adults
So, on your birthday web-based casinos will only wish you a happy birthday after you opt-in for the bonus. They do this using an opt-in feature that helps them remind themselves of . Ver mais
tibial torsion test name|femoral anteversion and tibial torsion